Springmvc请求参数的优雅处方式
当使用SpringMVC开发项目时,经常会出现对请求参数处理的困扰,例如:字符串前后端空格、前后端需要约定日期时间的传递方式、返回等。诸多问题我们的解决方式通常是前后端通过约定好统一的数据格式来保证系统暂时的稳定,或通过哪里出错改哪里的笨拙方式处理,这些都是不可取的。通过这篇文章,希望可以以优雅的方式彻底解决这个问题。
       当使用SpringMVC开发项目时,经常会出现对请求参数处理的困扰,例如:字符串前后端空格、前后端需要约定日期时间的传递方式、返回等。诸多问题我们的解决方式通常是前后端通过约定好统一的数据格式来保证系统暂时的稳定,或通过哪里出错改哪里的笨拙方式处理,这些都是不可取的。通过这篇文章,希望可以以优雅的方式彻底解决这个问题。
       我的老东家办公楼的最顶层有一处独特的景观,从正面顺楼梯直上是一处悬挂在半层的独立空间,在半层入口的对面即是出口,而出口被设计为一道滑梯。设计师在设计之处说道:“当你遇到困难和瓶颈时,不妨跳出你所在的维度到更高的维度去思考,上去坐坐,当你想出答案了,再顺着滑梯滑下来”。而此景观的名字源于爱因斯坦的一句话 问题往往在更高的维度可以得到解决,所以它的名字叫作高维之屋。

需求
去除请求参数中字符串两端空格。以该问题抛砖引玉
要去除请求参数中字符串两端的空格,涉及到两种情况:
- 1、URL参数
- 2、JSON请求体
对于第一种情况,通常在Get查询参数、PATH的路由参数中出现,在Controller的方法中以@RequestParam或@PathVariable注解变量完成参数绑定。对于第二种情况,通常在以Post请求的请求体中,在Controller的方法中以@RequestBody注解某实体完成参数绑定。
可以想到的解决方式如下:
- 方法一:接口调用方自行trim后传递。后端对接口调用方请求参数规范化程度不可控,所以不予考虑。
- 方法二:通过过滤器拦截请求参数,对字符串进行trim操作。在实现过滤器时,需要通过请求头content-type判断当前请求的内容格式,将请求对象中的参数取出trim后再塞回去,虽然可以实现需求,但编码实在太复杂,而且对于基于RESTful风格的URL中路由参数进行trim时处理起来更为复杂,且对于请求体中的JSON数据的值进行trim又涉及到递归的问题,所以仍不予考虑。
- 方法三:寻找Spring在Controller方法接收参数前的处理动作予以扩展。需要下点功夫看看官方文档啦~
解决方案
通过阅读Spring官方文档(4.3.24.RELEASE版本,有单页html和pdf版可供选择,以下简称官方文档)得知,SpringMVC在处理Controller方法参数时使用了Spring的参数绑定和类型转换机制,且对于处理以JSON数据格式的请求和响应(@RequestBody和@ResponseBody)采用Jackson来进行序列化和反序列化操作。从而可以得出一个推断,我只需要实现自定义参数绑定、自定义Jackson序列化和反序列化即可实现该需求,并且很优雅~
画外音:“哪有那么简单,想改你就改啊?”
画内音:“对于Spring这种级别的框架,一定是支持开发者进行自定义扩展的,况且我遇到的问题,社区内一定会有人比我遇到的早。”
画外音:“so?”
画内音:“so你个大头鬼,对任何问题一定要抱有乐观的态度,你特么就是一’锁’。”
画外音:“什么锁?”
画内音:“悲观锁!!!”
前50%:请求参数中字符串trim
1、啥是自定义数据绑定
官方文档的Method Parameters And Type Conversion小节介绍道:
String-based values extracted from the request including request parameters, path variables, request headers, and cookie values may need to be converted to the target type of the method parameter or field (e.g., binding a request parameter to a field in an @ModelAttribute parameter) they’re bound to. If the target type is not String, Spring automatically converts to the appropriate type. All simple types such as int, long, Date, etc. are supported. You can further customize the conversion process through a WebDataBinder (see the section called “Customizing WebDataBinder initialization”) or by registering Formatters with the FormattingConversionService (see Section 9.6, “Spring Field Formatting”).
大概意思是,在进行参数绑定的时候,若对应的绑定参数类型不是字符串(String),则Spring会自动将值转换为对应的类型,这个操作支持所有基础类型,例如:int、long、Date等。并且Spring提供了WebDataBinder作为自定义数据类型转换的扩展点。那么如何去扩展WebDataBinder呢?
官方文档的Customizing data binding with @InitBinder小节介绍道:
To customize request parameter binding with PropertyEditors through Spring’s WebDataBinder, you can use @InitBinder-annotated methods within your controller, @InitBinder methods within an @ControllerAdvice class, or provide a custom WebBindingInitializer. See the the section called “Advising controllers with @ControllerAdvice and @RestControllerAdvice” section for more details.
2、三种实现方法
Spring提供了三种方法来完成这件事儿:
- 可以在@Controller注解的类中使用
@InitBinder注解方法 - 在@ControllerAdvice注解的类中使用
@InitBinder注解方法 - 提供自定义
org.springframework.web.bind.support.WebBindingInitializer扩展
可以在@Controller或@ControllerAdvice注解的类中创建由@InitBinder注解的方法,或创建接口org.springframework.web.bind.support.WebBindingInitializer的实现类提供扩展。当时用@InitBinder注解方法时,该方法不可以有返回值,且参数可以是org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder、org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest和java.util.Locale的组合。就像下面这样:
1 |
|
但是,对于第一种方法,@InitBinder注解方法仅在当前@Controller中有效。(什么,那岂不是每个@Controller都得写一遍,我特么才不!)但提供自定义WebBindingInitializer扩展和在@ControllerAdvice注解的类中使用@InitBinder注解方法,则是全局配置(舒服~)
3、WebBindingInitializer接口
先看一下WebBindingInitializer接口是个啥
1 | public interface WebBindingInitializer { |
该接口已经为咱们定义好了初始化绑定器的方法,和使用@InitBinder注解方法从参数上来看只差Locale对象,可能是该对象用处不多吧。
来看看WebDataBinder对象,该对象内部有一个void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor propertyEditor)方法,其内部调用了PropertyEditorRegistry接口对象的void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor propertyEditor)方法,该方法的作用是为给定类型的所有属性注册给定的自定义属性编辑器,即我们可以为所有String、Date等类型的参数注册特定于该类型的属性编辑器。方法第一个参数为Class对象,我们可以提供任意类型,是任意类型哟,第二个参数为 这特么居然是Java类库自带的接口,通过IDEA找到该接口的子类,卧槽~java.beans.PropertyEditor属性编辑器对象,咿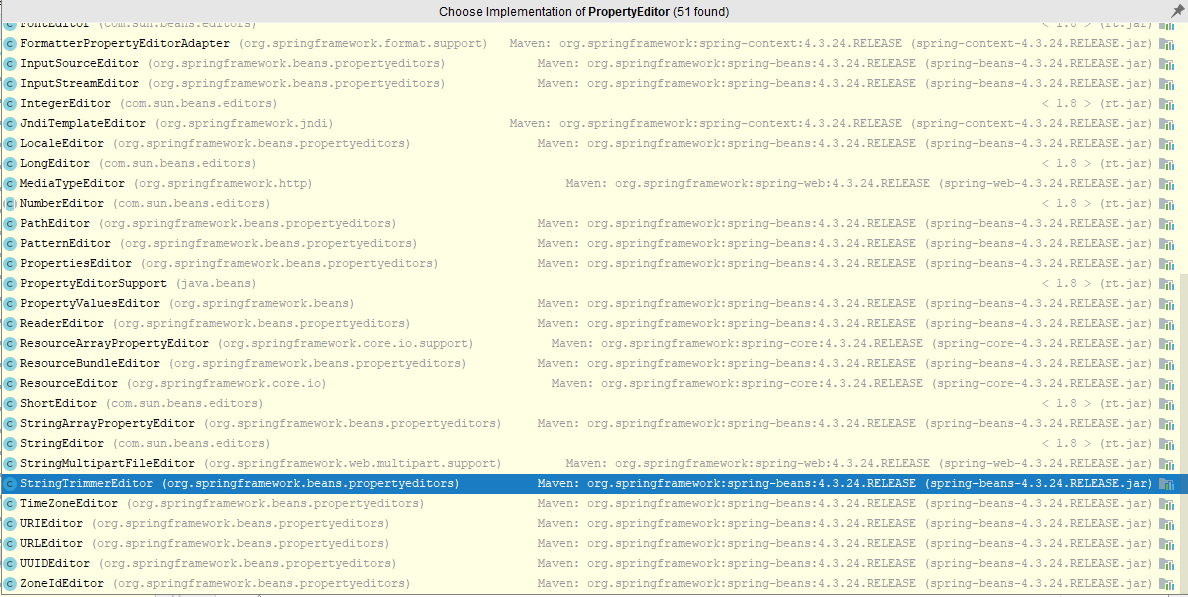
4、扩展WebBindingInitializer
二话不说,先来创建一个类,起一个一眼就能看出来和WebBindingInitializer有血缘关系的名字,并实现该接口重写initBinder方法,在该方法中使用WebDataBinder对象的registerCustomEditor方法为String类型的对象注册StringTrimmerEditor编辑器。
1 | public class CustomWebBindingInitializer implements WebBindingInitializer { |
5、配置WebBindingInitializer
定义好了扩展,该如何配置呢?官方文档Configuring a custom WebBindingInitializer 小节给出了方法,配置RequestMappingHandlerAdapterBean,将WebBindingInitializer对象配置到该Bean的webBindingInitializer属性。具体实现如下:
1 | <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"> |
此处有个坑,上述Bean的配置,要在启用SpringMVC注解配置<mvc:annotation-driven/>之前,否则不会生效。
6、测试字符串参数Trim效果
编写控制器,代码如下:
1 |
|
测试请求http://localhost:8080/tirm/param?p1=%20trim%20&p2=%2001%2000%201&p3=1.0%200020202002020202&p4=9999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999&p5=1.1111111111999000111111111111222222222222220200202020202020020202020202222
打印结果:
1 | String param is [trim] |
由打印结果可以看到,对于两端带空格的字符串,在进行参数绑定后,已经自动trim。
这仅仅实现了50%的工作量,另一部分,则是JSON中字符串值的trim。
后50%:请求体JSON中字符串trim
SpringMVC通过@RequestBody来处理application/json的HTTP请求,将json数据反序列化为某对象,已完成在Controller方法中使用对象接收请求体,常见使用场景如:新增实体、更新实体等。使用@ResponseBody将数据以Json形式发送给响应HTTP响应对象。我们从日常开发中得知,并且通过官方文档进一步证实SpringMVC使用Jackson处理以上的请求和响应。对于请求的json中数据的处理,必定要采用扩展Jackson的反序列化操作才可以优雅的实现,那么如何操作呢?在Spring项目开发当中,没有什么是文档和社区提供不了的。
1、Spring对请求响应的处理过程
首先看一下java中请求和响应的处理过程。Http请求和响应的报文其实都是字符串,请求和响应报文在java程序会被封装为ServletInputStream和ServletOutputStream流对象,从ServletInputStream中读取请求报文,从ServletOutputStream中输出响应报文。从流对象中只能读取到原始的字符串报文,同样输出流也是。那么在报文到达SpringMVC和从SpringMVC出去,都存在一个字符串到java对象的转化问题。这一过程,在SpringMVC中,是通过HttpMessageConverter这个对象来解决的。大概的处理过程如下: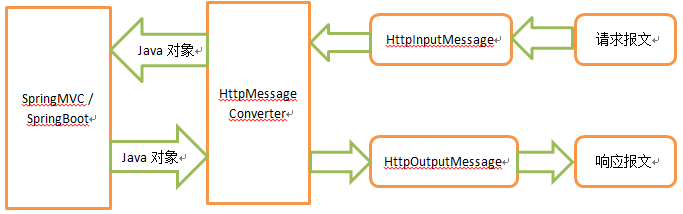
2、HttpMessageConverter
官方文档Enabling the MVC Java Config or the MVC XML Namespace 小节中提及到,使用<mvc:annotation-driven/>注解在DispatchServlet上下文中定义并弃用MVC的Java配置。开启该配置,会自动注册RequestMappingHandlerMapping,RequestMappingHandlerAdapter和ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver(以及其他),以支持使用带注释的控制器方法处理请求。
注意,此处添加该配置会自动注册
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,这就是为什么在上一节配置webBindingInitializer时RequestMappingHandlerAdapterBean对象要在<mvc:annotation-driven/>配置前书写的原因,因为后面的配置会不生效。
该配置还支持许多功能,详见官方文档该小节中列出的支持的功能列表。其中,HttpMessageConverter映入眼帘,正是刚刚所提及到的。
官方给出如下说明:
HttpMessageConverter support for @RequestBody method parameters and @ResponseBody method return values from @RequestMapping or @ExceptionHandler methods.
大意是HttpMessageConverter支持对@RequestBody注解的方法的参数以及@ResponseBody注解的方法的返回值进行处理。<mvc:annotation-driven/>配置默认启用了一下几种消息转换器:
- ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter converts byte arrays.
- StringHttpMessageConverter converts strings.
- ResourceHttpMessageConverter converts to/from org.springframework.core.io.Resource for all media types.
- SourceHttpMessageConverter converts to/from a javax.xml.transform.Source.
- FormHttpMessageConverter converts form data to/from a MultiValueMap<String, String>.
- Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter converts Java objects to/from XML — added if JAXB2 is present and Jackson 2
- XML extension is not present on the classpath.
- MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter converts to/from JSON — added if Jackson 2 is present on the classpath.
- MappingJackson2XmlHttpMessageConverter converts to/from XML — added if Jackson 2 XML extension is present on the classpath.
- AtomFeedHttpMessageConverter converts Atom feeds — added if Rome is present on the classpath.
- RssChannelHttpMessageConverter converts RSS feeds — added if Rome is present on the classpath.
通过该列表可以看到,对于JSON的处理,Spring提供了org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter转换器,看一下这是个什么玩儿楞~
3、MappingJackson2
该类的全限定类名为org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter,通过获取源码查看注释了解到,该转换器使用Jackson 2.x的ObjectMapper读写JSON,此转换器可用于反序列化为某类型的Java类或无类型的HashMap实例。 默认情况下,此转换器支持带有UTF-8字符集的application/json和application/*+json。可以通过设置该对象的supportedMediaTypes属性覆盖支持的media-type列表。下图是该转换器的UML图
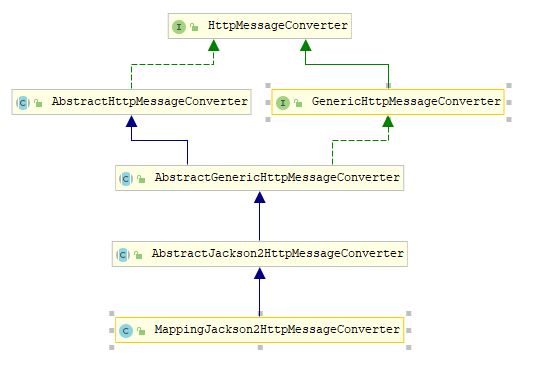
其直接父类org.springframework.http.converter.json.AbstractJackson2HttpMessageConverter内部实现如下:
1 | public abstract class AbstractJackson2HttpMessageConverter extends AbstractGenericHttpMessageConverter<Object> { |
看到在父类中有一个访问权限为protected的ObjectMapper类型对象,在刚刚了解到MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter转换器使用com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper对象对JSON进行读写,并且其父类还有对该对象的Setter方法,hie ~ hie ~ 又可以进行扩展啦
4、ObjectMapper是啥
来自官方的解释
ObjectMapper provides functionality for reading and writing JSON, either to and from basic POJOs (Plain Old Java Objects), or to and from a general-purpose JSON Tree Model (JsonNode), as well as related functionality for performing conversions.
ObjectMapper提供了从基本POJO(普通Java对象)或从通用JSON树模型(JsonNode)读取和写入JSON的功能,以及用于执行转换的相关功能。
这是个牛逼的角色,在Spring对JSON进行反序列化的时候,会使用消息转换器进行转换,那么内部实现就是通过该对象对JSON进行读取操作。通过阅读源码了解到,该类内部有一个<T> T readValue(JsonParser jp, Class<T> valueType)方法,该方法的作用是将JSON内容反序列化为Java对象、数组或包装类型。官方给出提示:
Note: this method should NOT be used if the result type is a container ({@link java.util.Collection} or {@link java.util.Map}. The reason is that due to type erasure, key and value types can not be introspected when using this method.
大意是,由于由于类型擦除的影响,对于java.util.Collection或java.util.Map类型,则不应使用此方法。
5、JsonParser是啥
ObjectMapper对象<T> T readValue(JsonParser jp, Class<T> valueType)方法第一个参数为com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonParser对象,他是用于读取JSON内容的公共API的基类,找到如下方法ObjectMapper registerModule(Module module);,该方法用于注册可以扩展由该映射器提供的功能,例如,通过添加自定义序列化和反序列化器,哎哟~ 小火鸡~~
该方法的参数为com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.Module接口对象,通过查找其子类发现就特么一个com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.module.SimpleModule类~看一下这个类都提供什么扩展点
SimpleModule addSerializer(Class<? extends T> type, JsonSerializer ser); // 为某类型添加序列化器 SimpleModule addDeserializer(Class type, JsonDeserializer<? extends T> deser); // 为某类型添加反序列化器
在添加反序列化器方法中,第二个参数为com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonDeserializer接口类型对象,阅读该接口源码文档发现该类的类注释写着大大的:
Custom deserializers should usually not directly extend this class, but instead extend {@link com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.std.StdDeserializer} (or its subtypes like {@link com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.std.StdScalarDeserializer}).
大意是自定义反序列化器通常不应直接扩展此类,而是扩展com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.deser.std.StdDeserializer(或其子类)
Ok~ 大致了解结构了吧,开干
6、扩展ObjectMapper
创建一个类,取一个一眼就能看出来和ObjectMapper有血缘关系的名字,并继承该抽象类,在该类初始化时注册扩展点。
1 | public class CustomObjectMapper extends ObjectMapper { |
通过org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter对象的messageConverters属性可以配置消息转换器,还记得前面我们讲的Spring提供的MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverterJSON消息转换器吗,就是他,他父类中的objectMapper参数可以配置ObjectMapper对象的扩展点,Perfect~ 配置如下
1 | <!--手动配置RequestMappingHandlerAdapter实现自定义扩展--> |
8、测试JSON的trim效果
1 | /** |
请求json:
1 | { |
后端解析后:
1 | {"name":"chenzhihao","phone":"12"} |